Nabto WebRTC Signaling
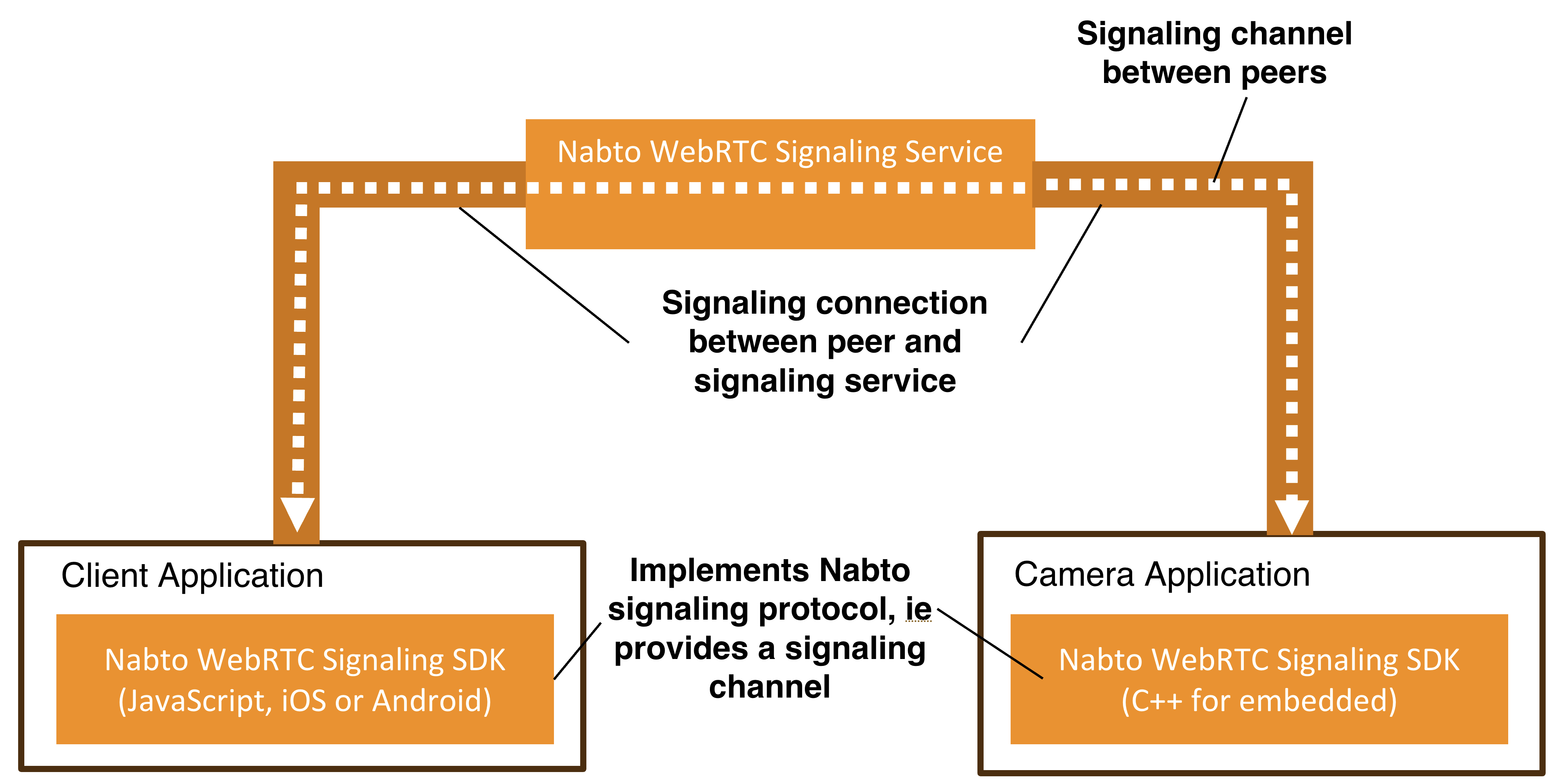
As described and motivated in the Platform Overview and with more details in the Application Development guide, the core feature of Nabto WebRTC is a signaling solution, enabling peers to exchange information that allows establishing a secure media connection.
Devices and Products
All communication through the Nabto WebRTC Signaling Service involves two peers: A client application and a connected device, typically a camera.
Each device is identified using a Product ID and a Device ID.
A Product is a logical grouping of devices managed under a shared configuration. It is created by the vendor and assigned a globally unique Product ID by the system. When a product is created, a geographic region is selected to host the signaling servers used for communication within that product.
A Device is an individual endpoint (e.g. a specific camera) identified by a unique Device ID within the product.
To securely connect to the signaling service, each device is provisioned with a private/public key pair. The public key is registered with the service and associated with the device’s Product ID and Device ID. See the security guide for more information about security in Nabto WebRTC.
While signaling is region-specific, all connections use Nabto’s globally distributed network of ICE servers to ensure optimal media performance regardless of peer location.
For practical details on how to configure products and devices, see the Signaling Configuration application guide.
Managed Nabto WebRTC Signaling Service
The Nabto WebRTC Signaling Service is fully managed and requires just simple configuration through the Nabto Cloud Console as seen in the application guide.
The signaling service is used with the Nabto WebRTC signaling protocol described in the next section. Applications are typically not aware of this communication: Nabto provides SDKs for all popular platforms that hides all protocol implementation details and and communication with the signaling service. This makes it simple to implement applications as seen in the application development guide.
The open signaling protocol is straightforward to implement, being based on a small set of JSON documents exchanged through HTTPS and websockets. Such custom implementation is relevant if support is needed for a target platform or application framework where Nabto does not provide an SDK. See links to the specification in the next section. The existing open source SDKs can be used as inspiration and guidance on structure.
Deployment
The Nabto WebRTC Signaling Service is available in high availability deployments in multiple geographical regions. When a Nabto WebRTC product is configured in the Nabto Cloud Console, it is decided in which region the devices (cameras) will be hosted.
The protocol
The Nabto WebRTC Signaling protocol is used between peers and the Nabto WebRTC Signaling service. The Nabto WebRTC Signaling service relays signaling messages between clients and devices (cameras) connected to the service. Devices are always authorized by the service based on public keys pre-configured in the backend. Clients are authorized towards devices using either central authorization or a shared secret approach.
The service also provides ICE server configuration to authorized peers. Clients that do not use central authorization (if using shared secrets instead), can request ICE credentials from the device (camera) which is always authorized.
For a peer to connect to the backend, it must first make an HTTP request to the Nabto WebRTC Signaling service. Based on the response, the peer will then be able to open a Websocket connection to the backend. The Websocket connection can then be used to relay signaling messages to other peers. ICE server configuration is requested using HTTP.
The HTTP requests towards the Nabto WebRTC Signaling service are described in the HTTP Protocol specification.
The messages exchanged through the relay using the resulting Websockets are described in the Websocket Protocol specification.
The protocol specification is only relevant as background information or if you want to make your own Nabto WebRTC Signaling protocol implementation, e.g. for a currently unsupported target platform or app framework. For most applications, the standard implementations provided by Nabto through the available SDKs are sufficient - see the Applications guide.
