Nabto WebRTC Client Applications
A Nabto WebRTC Client application is the initiator of a WebRTC session towards a device (camera), typically a mobile app or a browser based application.
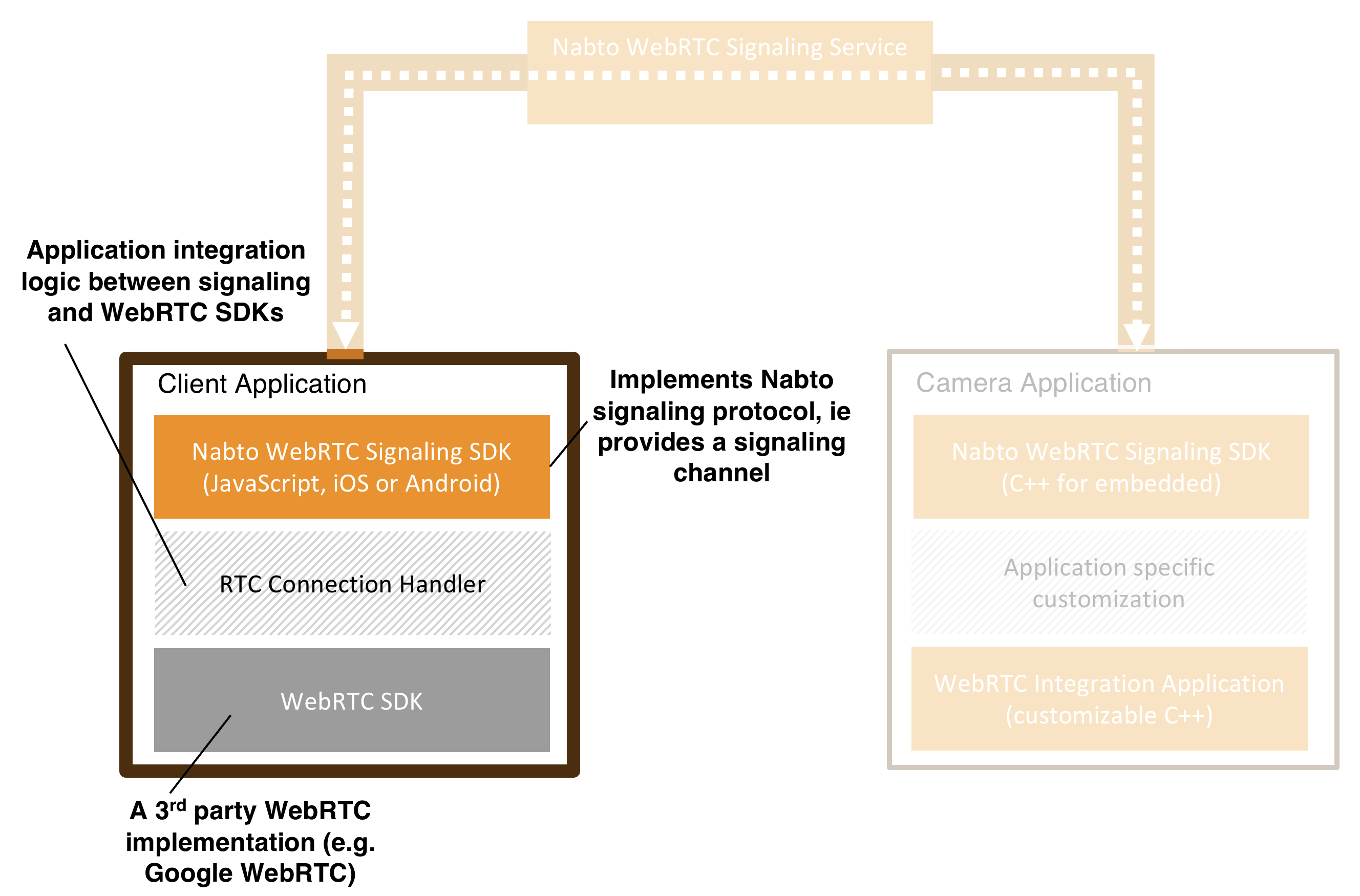
The application contains a few lines of code that ties the Nabto WebRTC Signaling SDK together with the chosen WebRTC SDK. This application specific code is denoted an RTCConnectionHandler in our examples and looks as follows:
class RTCConnectionHandler {
private let onTrackHandler: @escaping (RTCVideoTrack) -> Void
private var factory: RTCPeerConnectionFactory! = nil
private var signalingEventHandler: SignalingEventHandler? = nil
private var peerConnection: RTCPeerConnection? = nil
private var perfectNegotiation: PerfectNegotiation? = nil
private var signalingClient: SignalingClient? = nil
private var messageTransport: MessageTransport? = nil
init(
productId: String,
deviceId: String,
sharedSecret: String,
onTrackHandler: @escaping (RTCVideoTrack) -> Void
) async throws {
self.onTrackHandler = onTrackHandler
initPeerConnectionFactory() // Initializes self.factory
signalingClient = createSignalingClient( // [1]
SignalingClientOptions(
productId: productId,
deviceId: deviceId
)
)
do {
try await signalingClient?.start()
messageTransport = try await createClientMessageTransport( // [2]
client: signalingClient!,
options: .sharedSecret(sharedSecret: sharedSecret)
)
await messageTransport?.addObserver(self)
} catch {
print(error)
}
}
func initPeerConnectionFactory() {
RTCInitializeSSL()
let videoEncoderFactory = RTCDefaultVideoEncoderFactory()
let videoDecoderFactory = RTCDefaultVideoDecoderFactory()
self.factory = RTCPeerConnectionFactory(
encoderFactory: videoEncoderFactory, decoderFactory: videoDecoderFactory)
}
private func setupPeerConnection(_ iceServers: [SignalingIceServer]) {
let constraints = RTCMediaConstraints(mandatoryConstraints: nil, optionalConstraints: nil)
let config = RTCConfiguration()
config.iceServers = iceServers.map { iceServer in
RTCIceServer(
urlStrings: iceServer.urls,
username: iceServer.username,
credential: iceServer.credential
)
}
peerConnection = factory.peerConnection( // [4]
with: config,
constraints: constraints,
delegate: self
)
perfectNegotiation = PerfectNegotiation( // [5]
peerConnection: peerConnection,
messageTransport: messageTransport!
)
signalingEventHandler = SignalingEventHandler( // [6]
peerConnection: peerConnection,
client: signalingClient
)
signalingClient?.addObserver(signalingEventHandler!)
}
}
extension RTCConnectionHandler: MessageTransportObserver {
func messageTransport(
_ transport: any MessageTransport,
didGet message: WebrtcSignalingMessage
) async {
perfectNegotiation.onMessage(message)
}
func messageTransport(_ transport: any MessageTransport, didError error: any Error) async {
print("MessageTransport error: \(error)")
}
func messageTransport(
_ transport: any MessageTransport,
didFinishSetup iceServers: [SignalingIceServer]
) async {
setupPeerConnection(iceServers) // [3]
}
}
extension ViewController: RTCPeerConnectionDelegate {
func peerConnection(_ peerConnection: RTCPeerConnection, didGenerate candidate: RTCIceCandidate)
{
perfectNegotiation?.onIceCandidate(candidate)
}
func peerConnectionShouldNegotiate(_ peerConnection: RTCPeerConnection) {
perfectNegotiation?.onNegotiationNeeded()
}
func peerConnection(_ peerConnection: RTCPeerConnection, didChange newState: RTCIceConnectionState) {
signalingEventHandler?.handlePeerConnectionStateChange()
}
func peerConnection(
_ peerConnection: RTCPeerConnection, didAdd rtpReceiver: RTCRtpReceiver,
streams mediaStreams: [RTCMediaStream]
) {
if let track = rtpReceiver.track as? RTCVideoTrack {
self.onTrackHandler(track) // [7]
}
}
// ... remaining RTCPeerConnectionDelegate callbacks
}
class RTCConnectionHandler {
public interface OnTrackHandler {
void onTrack(VideoTrack track)
}
private PeerConnectionFactory peerConnectionFactory = null;
private PeerConnection peerConnection = null;
private EglBase eglBase = EglBase.create();
private OnTrackHandler onTrackHandler;
private SignalingEventHandler signalingEventHandler = null;
private PerfectNegotiation perfectNegotiation = null;
private SignalingClient client;
private MessageTransport messageTransport;
public RTCConnectionHandler(
String productId,
String deviceId,
String sharedSecret,
OnTrackHandler handler
) {
this.onTrackHandler = handler;
initPeerConnectionFactory(); // Initializes this.peerConnectionFactory
signalingClientOptions = new SignalingClientFactory.Options()
.setProductId(productId)
.setDeviceId(deviceId);
client = SignalingClientFactory.createSignalingClient(signalingClientOptions); //[1]
messageTransport =
ClientMessageTransport.createSharedSecretMessageTransport(client, sharedSecret); //[2]
messageTransport.addObserver(new MessageTransport.AbstractObserver() {
@Override
public void onWebrtcSignalingMessage(WebrtcSignalingMessage message) {
super.onWebrtcSignalingMessage(message);
this.perfectNegotiation.onMessage(message);
}
@Override
public void onSetupDone(List<SignalingIceServer> iceServers) {
super.onSetupDone(iceServers);
setupPeerConnection(iceServers); //[3]
}
});
}
private void initPeerConnectionFactory() {
var initOptions = PeerConnectionFactory
.InitializationOptions
.builder(this)
.createInitializationOptions();
PeerConnectionFactory.initialize(initOptions);
var encoderFactory = new DefaultVideoEncoderFactory(eglBase.getEglBaseContext(), true, true);
var decoderFactory = new DefaultVideoDecoderFactory(eglBase.getEglBaseContext());
peerConnectionFactory = PeerConnectionFactory.builder()
.setVideoEncoderFactory(encoderFactory)
.setVideoDecoderFactory(decoderFactory)
.createPeerConnectionFactory();
}
private void setupPeerConnection(List<SignalingIceServer> iceServers) {
var rtcIceServers = convertSignalingIceServersToPeerConnectionIceServers(iceServers);
var rtcConfig = new PeerConnection.RTCConfiguration(rtcIceServers);
var observer = new PeerConnection.Observer() {
@Override public void onRenegotiationNeeded() {
super.onRenegotiationNeeded();
perfectNegotiation.onNegotiationNeeded();
}
@Override public void onConnectionChange(PeerConnection.PeerConnectionState newState) {
super.onConnectionChange(newState);
this.signalingEventHandler.handlePeerConnectionStateChange();
}
@Override public void onIceCandidate(IceCandidate iceCandidate) {
super.onIceCandidate(iceCandidate);
perfectNegotiation.onIceCandidate(iceCandidate);
}
@Override public void onTrack(RtpTransceiver transceiver) {
super.onTrack(transceiver);
handleOnTrack(transceiver);
}
};
peerConnection = peerConnectionFactory.createPeerConnection(rtcConfig, observer); //[4]
this.perfectNegotiation = new PerfectNegotiation(peerConnection, messageTransport); //[5]
this.signalingEventHandler = new SignalingEventHandler(peerConnection, client); //[6]
client.addObserver(this.signalingEventHandler);
}
public void handleOnTrack(RtpTransceiver transceiver) {
if (transceiver != null) {
var receiver = transceiver.getReceiver();
if (receiver != null) {
var track = receiver.track();
if (track != null && Objects.equals(track.kind(), "video")) {
var videoTrack = (VideoTrack)track;
self.onTrackHandler(videoTrack) //[7]
}
}
}
}
private List<PeerConnection.IceServer> convertSignalingIceServersToPeerConnectionIceServers(List<SignalingIceServer> iceServers) {
return iceServers.stream().map(iceServer -> {
var builder = PeerConnection.IceServer.builder(iceServer.urls);
if (iceServer.username != null) { builder.setUsername(iceServer.username); }
if (iceServer.credential != null) { builder.setPassword(iceServer.credential); }
return builder.createIceServer();
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
class RTCConnectionHandler {
constructor({ productId, deviceId, sharedSecret, ontrack, logger, onerror }) {
this.signalingClient = SDK.createSignalingClient({ // [1]
productId: productId,
deviceId: deviceId,
requireOnline: true
});
this.ontrack = ontrack;
this.logger = logger;
this.onerror = onerror;
this.messageTransport = SDK.createClientMessageTransport(this.signalingClient, { // [2]
securityMode: SDK.ClientMessageTransportSecurityMode.SHARED_SECRET,
sharedSecret: sharedSecret,
})
this.messageTransport.on("setupdone", async (iceServers) => {
this.createPeerConnection(iceServers); // [3]
})
this.messageTransport.on("error", (error) => {
this.onerror(error)
})
this.signalingClient.on("error", (error) => {
this.onerror(error)
})
this.signalingClient.on("connectionstatechange", () => {
this.logger(`New SignalingClient connection state: ${this.signalingClient.connectionState}`)
})
this.signalingClient.start();
}
async createPeerConnection(iceServers) {
this.pc = new RTCPeerConnection({ iceServers: iceServers }); // [4]
this.perfectNegotiation = new SDK.PerfectNegotiation(this.pc, this.messageTransport); // [5]
this.signalingEventHandler = new SDK.SignalingEventHandler(this.pc, this.signalingClient); // [6]
this.pc.ontrack = (event) => {
this.ontrack(event) // [7]
}
this.pc.onconnectionstatechange = () => {
this.logger(`New RTCPeerConnection state: ${this.pc.connectionState}`)
}
}
}
The following notes clarify the most important parts of the above client application code:
[1]: The SDK’s signaling client is created with createSignalingClient(). It connects to the Nabto WebRTC Signaling service and sends signaling messages to it which in turn passes these on to the target device.
[2]: The Nabto WebRTC Signaling protocol is implemented by the messageTransport created by createClientMessageTransport(). It encodes and signs messages according to the protocol definition, ie it implements a logical signaling channel.
[3]: When the setupdone event is fired by the messageTransport, the signaling channel is ready to use.
[4]: The RTCPeerConnection is a core component provided by WebRTC SDK (e.g. the browser) to establish, negotiate and manage a peer-to-peer connection. It handles media and data transmission, ICE candidates and encryption.
[5]: The PerfectNegotiation helper implements Perfect Negotiation to avoid offer collisions (glare) when both peers try to initiate a connection at the same time (especially relevant in camera scenarios if using WebRTC Data Channels). The helper manages signaling state and handles session description and ICE candidate exchange through the messageTransport.
[6]: The SignalingEventHandler observes both RTCPeerConnection state and signaling reconnect events. It automatically triggers ICE restarts or connection health checks when needed, ensuring robustness in unreliable or mobile networks.
[7]: The ontrack handler receives incoming media streams. When the remote peer adds a track, this callback is triggered, allowing the application to render or process the incoming audio/video stream.
Setting up the a live stream using this class then looks as follows:
let videoView: RTCMTLVideoView = ... // This should be your RTCMTLVideoView from your UI
let connection = try await RTCConnectionHandler(
productId: productId = "wp-39wu7tex",
deviceId: deviceId = "wd-3xtqp3hy4xxy3av3",
sharedSecret: sharedSecret = "59470b3f8e331d9975da366d8dc0dcf743ef6a1154a4f779932740b4d14be3ab",
onTrackHandler: { track in
track.add(videoView)
}
)
private void createConnectionHandler() {
// This should be a view that implements org.webrtc.VideoSink
VideoSink videoView = ...;
RTCConnectionHandler connection = new RTCConnectionHandler(
"wp-39wu7tex",
"wd-3xtqp3hy4xxy3av3",
"59470b3f8e331d9975da366d8dc0dcf743ef6a1154a4f779932740b4d14be3ab",
(track) -> { track.add(videoView) }
);
}
const connection = new RTCConnectionHandler({
productId: "pr-39wu7tex",
deviceId: "de-3xtqp3hy4xxy3av3",
sharedSecret: "59470b3f8e331d9975da366d8dc0dcf743ef6a1154a4f779932740b4d14be3ab",
ontrack: (track) => {
const videoElement = document.getElementById("remote-video");
if (videoElement.srcObject === null) {
videoElement.srcObject = new MediaStream();
}
videoElement.srcObject.addTrack(track.track);
},
logger: console.log,
onerror: (err) => {
console.error("WebRTC error:", err);
}
});
