Baseline Security in WebRTC
Security Guarantees in the WebRTC Standard
The standardized WebRTC protocol is designed with strong, built-in security guarantees for real-time media and data transmission between peers. All WebRTC connections are end-to-end encrypted by default using industry-standard protocols. Media streams are protected through DTLS-SRTP (Datagram Transport Layer Security with Secure Real-time Transport Protocol), while data channels use SCTP over DTLS. Both ensure confidentiality, integrity and authentication of the communication path.
A critical feature of WebRTC security is peer fingerprint validation. Each peer generates a DTLS public/private key pair as part of peer connection initialization. A fingerprint of the DTLS certificate is embedded in the SDP (Session Description Protocol) offer or answer and exchanged via signaling.
Before any media is accepted, both peers validate the remote fingerprint against the certificate presented during the DTLS handshake. This prevents man-in-the-middle attacks by binding the session to known public keys. However, since the fingerprints are exchanged through the signaling channel, this relies on a secure signaling channel.
Nabto WebRTC Specifics
In Nabto WebRTC Signaling, the fingerprints are embedded automatically by the underlying WebRTC implementation (e.g. browser or native stack) and transmitted through the SDK’s signaling transport, coordinated by the Perfect Negotiation implementation. The SDP messages carrying the fingerprints are exchanged securely using the Nabto WebRTC Signaling protocol. The signaling exchange is secured with TLS (see below) and either Centralized Authorization or Shared Secret Authentication. This ensures the signaling channel and, by extension, the resulting WebRTC connection can be trusted.
Securing Signaling Communication
While the WebRTC standard fully specifies how to secure the media and data path, it does not define how signaling should be implemented or secured. Signaling is the process by which peers exchange metadata required to set up the WebRTC connection, such as session descriptions and ICE candidates. Nabto WebRTC Signaling is an example of such signaling implementation.
Nabto WebRTC Specifics
Nabto WebRTC uses TLS-protected connections for signaling, with TLS handled by the underlying platform or standard libraries. This follows the standard practice used by most production-ready WebRTC solutions. TLS ensures that signaling messages remain confidential and tamper-proof during transit, providing both confidentiality and integrity.
The WebRTC security model assumes that if the signaling channel is secure and the exchanged fingerprints are trusted, the resulting media connection can be trusted as well.
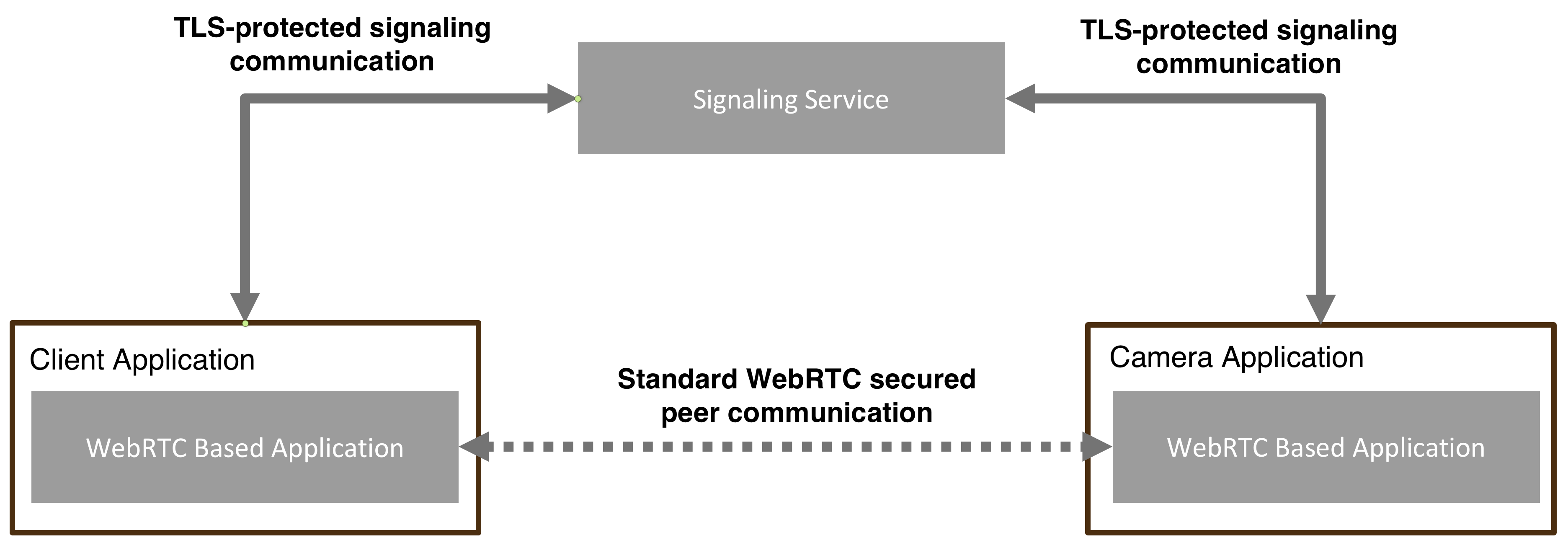
The WebRTC standard, combined with TLS-protected signaling, provides a strong foundation for secure communication. However, a complete solution also requires authentication and authorization of signaling peers: Is the user or camera really who they claim to be? Should this specific user be allowed to open a WebRTC connection to this camera? Nabto WebRTC Signaling provides robust and easy-to-use mechanisms for authentication and authorization, as outlined in the Camera Authentication, Central Authorization and Shared Secret Authentication sections.
