Developing a Nabto WebRTC Application
This section provides an overview of the structure and components involved when developing applications using the Nabto WebRTC Signaling SDKs.
The figure below shows a high-level architecture of a typical Nabto WebRTC application setup:
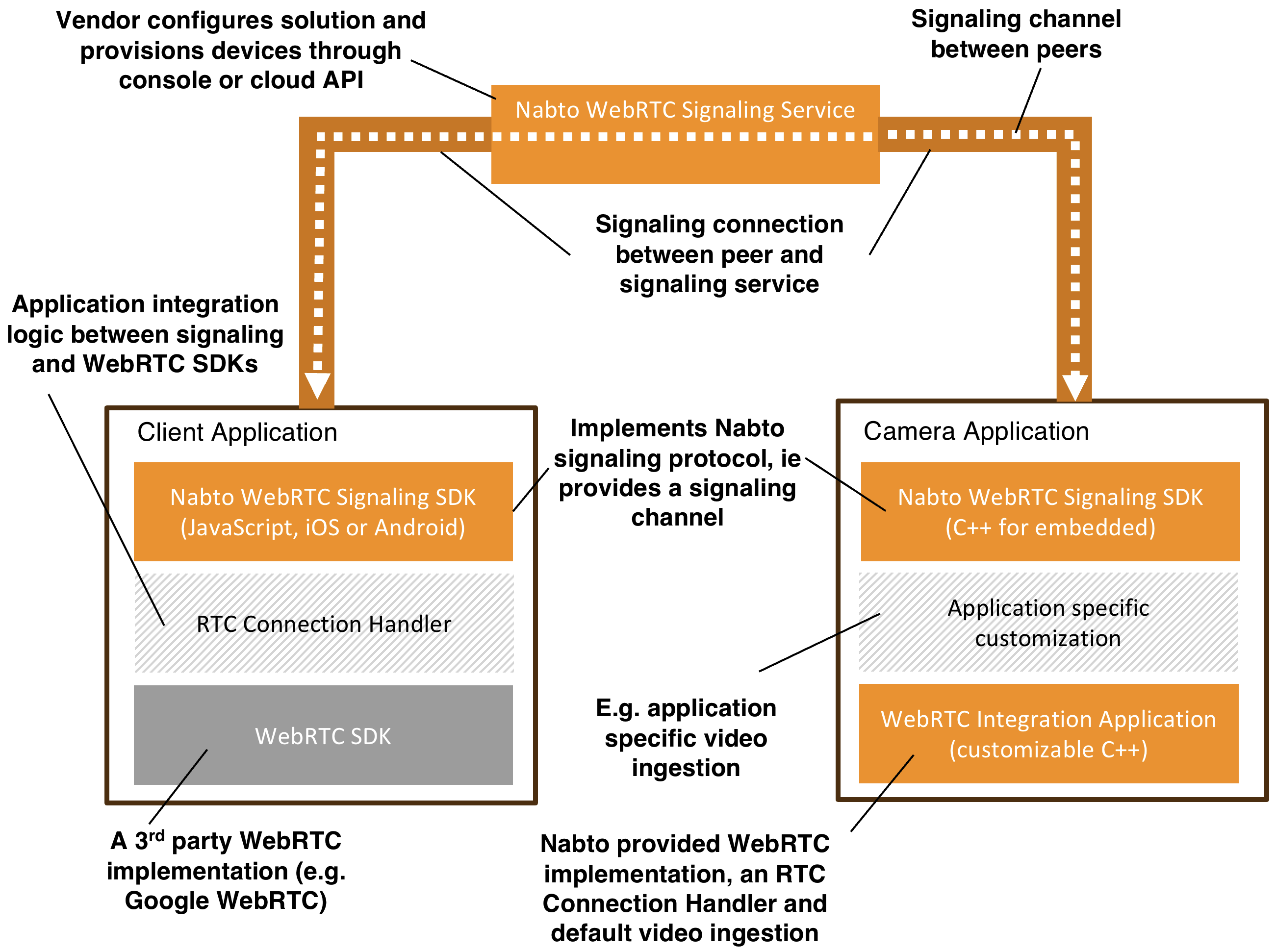
Orange boxes are components and services provided by Nabto as part of the Nabto WebRTC platform. Light grey boxes are implemented by the vendor. The dark grey box is a 3rd party standard implementation, ie part of the browser or a standalone SDK like Google’s WebRTC SDK.
Overview
A complete Nabto WebRTC solution consists of:
- The Nabto WebRTC Signaling Service: Coordinates session setup between peers. Configurable through the Nabto Cloud Console and the backend REST APIs for integration with the vendor’s own backend and/or manufacturing process.
- ICE servers (STUN/TURN): Enable peers to establish direct or relayed WebRTC connections across NATs and firewalls. Nabto provides managed ICE (STUN/TURN) services through Nabto WebRTC ICE, but vendors are free to use their own infrastructure. Also, Nabto WebRTC ICE can be used with the vendor’s own signaling solution, ie independent of Nabto WebRTC Signaling if so desired.
- A client application, such as a mobile app or web application developed using the Nabto WebRTC Client SDK.
- A camera (device) application acting as the passive peer device. This is based on the Nabto WebRTC Device SDK. Standard Nabto WebRTC Integration Applications exists that can be used as is or customized.
- Optional: Authorization service if using Central Authorization for access control, the vendor must provide a service for issuing tokens that grant the individual client access to requested devices.
